Some breast cancer patients can retain lymph nodes, avoiding lymphedema
Removal of armpit lymph nodes can leave many breast cancer patients with lingering lymphedema, a painful and unsightly swelling of the arm.
Apr 13, 2024
0
16
Removal of armpit lymph nodes can leave many breast cancer patients with lingering lymphedema, a painful and unsightly swelling of the arm.
Apr 13, 2024
0
16

Throat cancer is one of the fastest-growing cancers, and it is often linked to HPV. Oropharyngeal cancer, or throat cancer, is a type of head and neck cancer that can be divided into two subgroups: HPV-associated cancers ...
Apr 10, 2024
0
1

AZD1390, an ataxia telangiectasia mutant (ATM) kinase inhibitor, demonstrated a manageable safety profile in both recurrent and newly diagnosed glioblastoma (GBM) patients when given in combination with standard-of-care radiotherapy ...
Apr 9, 2024
0
1

While kidney cancer is rare in children, Wilms tumor is the most common type found in kids, with between 500 and 600 children diagnosed annually in the U.S. The disease most often affects kids ages 3 to 4.
Apr 8, 2024
0
0

Researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center showed that altering the sequence of breast cancer treatment to administer radiation before mastectomy allowed for concurrent breast reconstruction surgery, ...
Apr 5, 2024
0
25

It is possible to leave most of the lymph nodes in the armpit, even if one or two of them have metastases larger than two millimeters. This is shown in a trial enrolling women from five countries, led by researchers at Karolinska ...
Apr 4, 2024
0
0

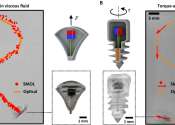
In the medicine of the future, tiny robots will navigate independently through tissue and medical instruments will indicate their position inside the body during surgery. Both require doctors to be able to localize and control ...
Apr 2, 2024
0
2
Cancer patients about to undergo radiation oncology treatment have lots of questions. Could ChatGPT be the best way to get answers?
Apr 2, 2024
0
15

If improving your outlook on life really was as simple as "don't worry, be happy," then keeping your spirits up would be a piece of cake. Unfortunately, it's not so simple, as a multitude of factors beyond our control can ...
Apr 1, 2024
0
2

An estimated 2.2 million people suffer from lung cancer worldwide, making it the second most common type of cancer. Though improvements in treatment have been made, the overall survival rate of lung cancer patients is low, ...
Mar 27, 2024
0
3

In physics, radiation describes any process in which energy emitted by one body travels through a medium or through space, ultimately to be absorbed by another body. Non-physicists often associate the word with ionizing radiation (e.g., as occurring in nuclear weapons, nuclear reactors, and radioactive substances), but it can also refer to electromagnetic radiation (i.e., radio waves, infrared light, visible light, ultraviolet light, and X-rays) which can also be ionizing radiation, to acoustic radiation, or to other more obscure processes. What makes it radiation is that the energy radiates (i.e., it travels outward in straight lines in all directions) from the source. This geometry naturally leads to a system of measurements and physical units that are equally applicable to all types of radiation.
This text uses material from Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY-SA