Fate of the heart: Researchers track cellular events leading to cardiac regeneration
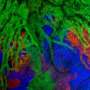
In a study published in the June 19 online edition of the journal Nature, a scientific team led by researchers from the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine visually monitored the dynamic cellular events that take place when cardiac regeneration occurs in zebrafish after cardiac ventricular injury. Their findings provide evidence that various cell lines in the heart are more plastic, or capable of transformation into new cell types, than previously thought.
More importantly, the research reveals a novel potential source of cells for regenerating damaged heart muscle, according to principal investigator Neil Chi, MD, PhD, assistant professor of medicine in the Division of Cardiology and member of the Institute of Genomic Medicine at UC San Diego.
Heart failure remains the leading cause of death in the developed world, largely due to the inability of mammalian hearts to regenerate new cells and repair themselves. However, lower vertebrates such as zebrafish are capable of generating new ventricular heart muscle cells, or cardiomyocytes, that can replace the heart muscle lost through ischemia-induced infarcts – more commonly known in humans as heart attacks.
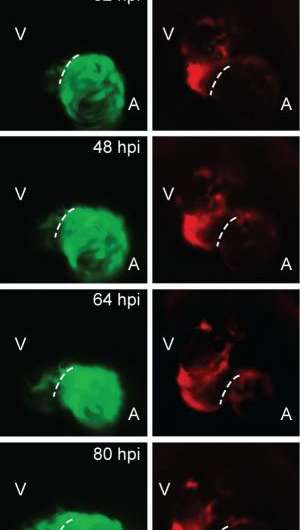
In this study, the scientists generated a genetic ablation system in zebrafish capable of targeted destruction of heart muscle, and then tracked both atrial and ventricular cardiomyocytes during injury using fluorescent proteins.
Using a genetic fate mapping technique – a method of comparing cells at various points of development in order to understand their cellular embryonic origin – the scientists revealed that cardiomyocytes in the heart's atrium can turn into ventricular cardiomyocyctes in a process called transdifferentiation. This transdifferentiation allows the atrial cells to regenerate and repair the ventricle, which is the chamber primarily affected in heart attacks.
First author Ruilin Zhang noted that such transdifferentiation was blocked when Notch signaling was inhibited, and subsequent studies will look at the Notch signaling pathway to understand the underlying mechanism at work.
"This is among the first studies to look at these specific cardiac lineages in detail to see how zebrafish are able to regenerate heart cells," said Chi, adding that their findings open a door to revealing how such regeneration might someday work to change the fate of human hearts.
More information: dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature12322