Research offers a new approach to improving HIV vaccines
In a scientific discovery that has significant implications for preventing HIV infections, researchers at Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute (Sanford-Burnham) have identified a protein that could improve the body's immune response to HIV vaccines and prevent transmission of the virus.
The study shows how a protein called polyglutamine-binding protein 1 (PQBP1) acts as a front-line sensor and is critical to initiating an immune response to HIV. When the PQBP1 encounters the virus, it starts a program that triggers an overall protective environment against infection and enhances the production of virus-specific antibodies. The research, which identified PQBP1 as a target for improving HIV vaccines, was published June 4 online ahead of print in the journal Cell.
'Vaccines work by teaching the immune system to react by mimicking a natural infection,' said lead author Sunnie Yoh, Ph.D., a postdoctoral fellow in the lab of Sumit Chanda, Ph.D., director of the Immunity and Pathogenesis Program at Sanford-Burnham. 'Designing a drug that mimics the interface between HIV and PQBP1 would allow an HIV vaccine to more effectively re-create an immune environment that mirrors real infection.'
'Current approaches to HIV vaccine development have thus far yielded little fruit, partly because of the lack of an effective vaccine adjuvant. Adjuvants promote a robust immune response to vaccines and are critical to eliciting long-lasting immunity,' said Chanda. 'Our study identifies a promising new target for a vaccine adjuvant that could advance the development of HIV vaccines and prevent infection.'
How it works
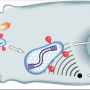
Although the major target of HIV infection is CD4+ T cells, dendritic cells are one of the first cell types to encounter HIV during sexual transmission. After HIV infects cells, its DNA forms an interface with PQBP1 in sentinel dendritic cells and initiates the immune response.
Dendritic cells control the innate immune response—a generic, non-specific defense against pathogens. These cells also activate the adaptive immune response that generates highly specific antibodies that provide protective, long-lasting immunity. Both the innate and adaptive immune systems are necessary to provide an optimal immune response to vaccines.
'PQBP1 acts as a sentry for innate immune response to HIV. The development of a highly effective HIV vaccine will likely depend on both combining the correct immunogens, which are viral proteins, and unlocking the innate response, to establish long-lived protection,' said Chanda. 'Now that we know the gatekeeper, it will be much easier to find a key.'