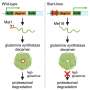
A natural history of neurons: Diverse mutations reveal lineage of brain cells
Walt Whitman's famous line, "I am large, I contain multitudes," has gained a new level of biological relevance.
As we grow, our brain cells develop different genomes from one another, according to new research from Harvard Medical School and Boston Children's Hospital.
The study, published Oct. 2 in Science, shows for the first time that mutations in somatic cells—that is, any cell in the body except sperm and eggs—are present in significant numbers in the brains of healthy people. This finding lays the foundation for exploring the role of these post-conception mutations in human development and disease.
"A lot of people have been asking lately whether somatic mutations contribute to a range of neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative diseases, but they couldn't answer the question because of the limitations of technology," said the study's co-senior author, Peter Park, associate professor of biomedical informatics at HMS.
The research team was able to make headway on the problem by combining single-cell genome sequencing with rigorous data analysis techniques.
Already, the researchers have discovered that somatic mutations appear to occur more often in the genes a neuron uses most. They have also been able to trace brain cell lineages based on patterns of mutation.
"These mutations are durable memory for where a cell came from and what it has been up to," said the study's co-senior author, Christopher A. Walsh, the HMS Bullard Professor of Pediatrics and Neurology and chief of the Division of Genetics and Genomics at Boston Children's. "This work is a proof of principle that if we wanted to, and if we had unlimited resources, we could actually decode the whole pattern of development of the human brain."
"I believe this method will also tell us a lot about healthy and unhealthy aging as well as what makes our brains different from those of other animals," Walsh added.
Taking a history
Germline, or inherited, mutations have taken most of the blame for causing diseases and disorders of the brain, including Alzheimer's, autism and schizophrenia. The role of non-inherited mutations in somatic cells has been murkier. Until recently, scientists didn't even know if they existed in the brain in amounts great enough to matter.
"Single-cell technology was essential for finding them," said Walsh.
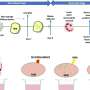
Walsh, Park and team studied a particular kind of somatic mutation called single nucleotide variants. Each variant may occur in just a few cells, or even just one, so they can be hard to detect with whole-genome sequencing analyses that average hundreds of thousands of cells. Sequencing individual cells brings the rare mutations to light.
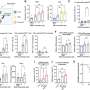
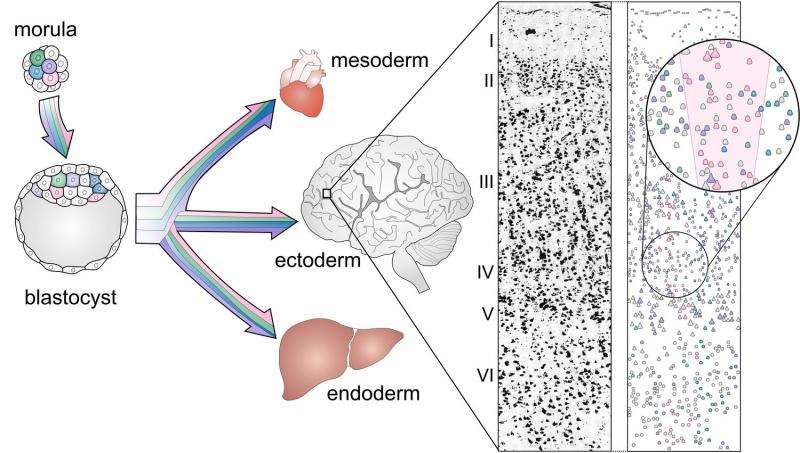
The downside is that it costs just as much to sequence the genome of one cell as it does to sequence the genome of an entire person. Working within this limitation, the researchers were able to sequence 36 neurons sampled from the cerebral cortices of three deceased people without brain disease, aged 15, 17 and 42.
The researchers found that each neuron contained about 1,500 single nucleotide variants.
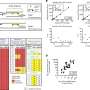
For each person, the researchers compared the neurons' genetic sequences to one another and to the individual's heart cells. This allowed them to start figuring out which mutations were shared by which neurons and which could be found elsewhere in the body. They then conducted tests in several parts of the brain to see how many cells in each region carried the same mutations as the neurons they'd sequenced.
Grouping neurons based on their mutations provided clues about cell history, because neurons that shared mutations likely came from the same stem-cell ancestor. If only a few cells shared a mutation, they probably belonged to a lineage that split more recently.
"If a mutation arose very early, it would be present both inside and outside the brain. Or if it arose later, it would be in certain parts of the brain and not others," said Walsh. "We're looking at a record of the series of cell divisions that generated the brain."
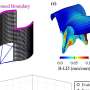
Based on patterns of mutation as well as location in the brain, some neurons' lineages could be traced back to a specific day during embryonic development.
Use it and lose it
Many phenomena can create somatic mutations. Ultraviolet light causes them in skin cells. Errors in DNA replication cause them in rapidly dividing cancer cells.
"What we found in the brain was neither of those things," said Walsh. "We thought the dominant source of mutation would be faulty DNA replication and were surprised to find that instead, it's faulty DNA expression."
Park's data analysis revealed that the genes with the most mutations tended to be the ones that were used most in the brain.
"People like to say about your brain, 'use it or lose it.' Unfortunately, we found there's a certain element of 'use it and lose it,'" said Walsh. "Every time you turn on a gene, there is at least some level of risk."
The findings make the team wonder whether somatic mutations accumulate with age and might contribute to neurodegeneration. They plan to investigate how, when and why these mutations arise in the brain; explore whether having a variety of mutations is damaging or protective; determine if mutation rates vary from person to person; and study additional types of somatic mutations in the brain and other tissues.
As he helps to uncover the role of somatic mutations in the brain, Park has taken in stride the knowledge that our brains contain a multitude of genetic variation.
"I'm full of mutations but I'm walking around, pretty healthy," said Park. "It just goes to show that there are a lot of things we don't understand."
More information: Somatic mutation in single human neurons tracks developmental and transcriptional history, Science, www.sciencemag.org/lookup/doi/ … 1126/science.aab1785