Scientists reveal how animals find their way 'in the dark'
Scientists have revealed the brain activity in animals that helps them find food and other vital resources in unfamiliar environments where there are no cues, such as lights and sounds, to guide them.
Animals that are placed in such environments display spontaneous, seemingly random behaviors when foraging. These behaviors have been observed in many organisms, although the brain activity behind them has remained elusive due to difficulties in knowing where to look for neural signals in large vertebrate brains.
Now, in a study to be published in the journal eLife, researchers have used whole-brain imaging in larval zebrafish to discover how their brain activity translates into spontaneous behaviors. They found that the animals' behavior in plain surroundings is not random at all, but is characterized by alternating left and right turn "states" in the brain, where the animals are more likely to perform repeated left and right turning maneuvers, respectively.
"We noted that a turn made by the zebrafish was likely to follow in the same direction as the preceding turn, creating alternating "chains" of turns biased to one side and generating conspicuous, slaloming swim trajectories," says first author Timothy Dunn, a postdoctoral researcher at Harvard University.
"Freely swimming fish spontaneously chained together turns in the same direction for approximately five to 10 seconds on average, and sometimes for much longer periods. This significantly deviates from a random walk, where movements follow no discernible pattern or trend."
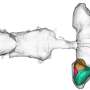
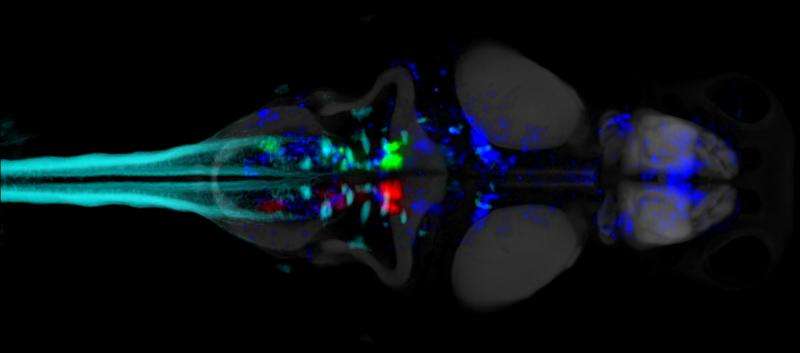
By analyzing the relationship between spontaneous brain activity and spontaneous behavior in the larval zebrafish, the researchers generated whole-brain activity maps of neuronal structures that correlated with the patterns in the animals' movements.
They discovered a nucleus in the zebrafish hindbrain, which participates in a simple but potentially vital behavioral algorithm that may optimize foraging when there is little information about the environment available to the animal.
As such behavioral strategies must exist in other animals that explore environments much larger than themselves, the team expects that the neural systems observed in the zebrafish must also exist in other organisms.
"Overall, our whole-brain analysis, neural activity experiments, and anatomical characterization of zebrafish revealed a circuit contributing to the patterning of a spontaneous, self-generated behavior," explains co-first author Yu Mu, a postdoctoral researcher at Janelia Research Campus.
"As our study makes very specific predictions about this circuit, future experiments will be required to validate its critical components. It will also be interesting to see if different environmental contexts and the motivational state of zebrafish influence their spontaneous swim patterns."
More information: Timothy W Dunn et al. Brain-wide mapping of neural activity controlling zebrafish exploratory locomotion, eLife (2016). DOI: 10.7554/eLife.12741
Journal information: eLife
Provided by eLife