Respiratory microbiome may influence inflammation in CF
(HealthDay)—Reduced bacterial diversity in the upper and lower airways in infants with cystic fibrosis (CF) is associated with use of prophylactic antibiotics and younger age at sampling, while less diversity in lavage samples is associated with lower inflammation, according to a study published online July 14 in the Annals of the American Thoracic Society.
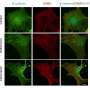
Jessica E. Pittman, M.D., from Washington University in St. Louis, and colleagues enrolled infants with CF in a prospective, observational study to examine the bacterial microbiota and inflammatory profiles of the respiratory tract. Thirty-two infants underwent bronchoalveolar lavage and oropharyngeal sampling. The authors measured bacterial diversity and density (load), and analyzed lavage samples for inflammatory markers in the epithelial lining fluid.
The researchers observed a strong correlation in Shannon diversity between upper and lower airway samples from a given subject, although the community compositions differed. Younger subjects and those receiving daily anti-staphylococcal antibiotic prophylaxis had lower microbial diversity. Reduced diversity in lavage samples correlated with lower interleukin-8 concentration and absolute neutrophil count.
"Our findings suggest modification of the respiratory microbiome in infants with CF may influence airway inflammation," the authors write.
One author disclosed financial ties to Eli Lilly.
More information:
Abstract
Full Text (subscription or payment may be required)
Copyright © 2017 HealthDay. All rights reserved.