First integrated atlas of microRNA expression in human primary cells
The human body consists of hundreds of different cell types with very different functions and behaviors, despite the fact that the genome sequence of almost all cells of an individual person is identical. The variation in functional roles of cells is accomplished by an intricate regulatory network consisting of regulatory proteins as well as regulatory RNAs such as microRNAs. Dysregulation of such networks plays a major role in disease development, in particular in cancer.
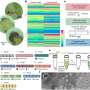
FANTOM, an international scientific consortium led by RIKEN, has now created the first extensive atlas of microRNA expression in human primary cells. Leveraging the collection of RNA samples established as part of the fifth edition of FANTOM, the team has sequenced microRNA libraries of hundreds of human samples, including many cell types for which the microRNA presence had never been investigated before.
In earlier stages of the FANTOM project, each of the samples had been profiled using Cap Analysis Gene Expression (CAGE), a technology developed at RIKEN to discover the precise starting site of RNAs. Combining the CAGE data with microRNA data allowed the team to create an integrated atlas of microRNA expression as well as a map of the genomic regions that control the expression of microRNAs in different cell types. Together, these data sets provide a first view of how these regulators contribute the establishing the unique identity of each cell type in the human body.
In the research published in Nature Biotechnology, the scientists showed that the genomic control regions of microRNAs identified in this study were highly conserved in evolution, underlining their importance in cellular regulation. The researchers also found thousands of new genomic loci producing short RNAs, which may prove to constitute a novel class of regulatory short RNAs.
Michiel de Hoon of the RIKEN Center for Life Science Technologies says, "We have made the expression atlas available online, and expect to have thousands of users all around the world. We believe it will be an essential resource for understanding microRNA regulation and its role in human disease."
More information: An integrated expression atlas of miRNAs and their promoters in human and mouse, Nature Biotechnology (2017). DOI: 10.1038/nbt.3947
The atlas is available at fantom.gsc.riken.jp/5/suppl/De_Rie_et_al_2017/
Journal information: Nature Biotechnology
Provided by RIKEN