Study establishes oxytocin uptake by infants via breastfeeding
Oxytocin is a peptide hormone important in establishing good communication with others. It is therefore considered to be indispensable to the development of the social brain. Oxytocin is secreted into the entire brain and the bloodstream.
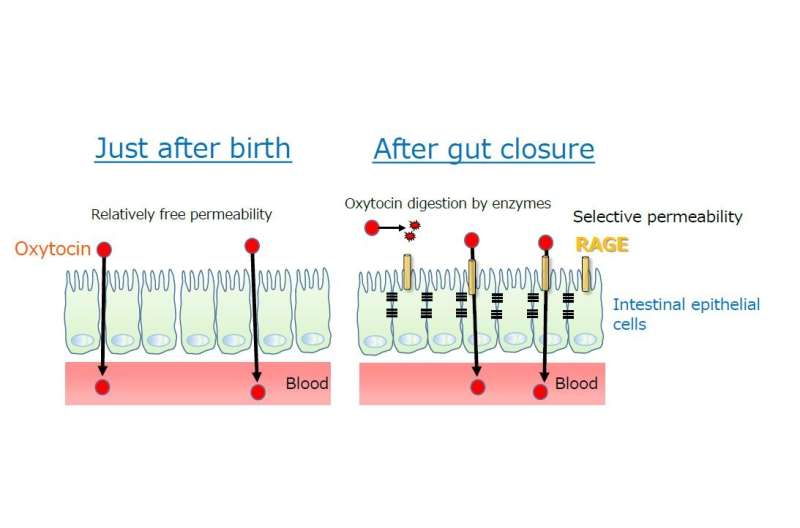
Mother's milk contains nutrients including oxytocin, which is derived from the blood. The digestive tract forms a barrier to avoid uptake of undesirable macromolecules soon after birth. Therefore, it was thought that oxytocin would not be freely permeable from the digestive tract. On the other hand, the oxytocin level in the blood of babies drinking mother's milk has been found to be elevated, suggesting oxytocin could somehow be transported even in the presence of such a barrier.
Breastfeeding has been recommended by the WHO since 2007 because of its positive effects on babies' short-term and long-term health, but decreasing numbers of mothers are breastfeeding for 12 months. On the other hand, production of powdered milk has increased year after year, forming a 7 trillion dollar market worldwide. In the United States, 13 percent of babies are born prematurely, and the number of babies around the globe who are born prematurely or with a very low body weight is approximately 15 million annually. Researchers now note the importance of giving those babies colostrum and raising them with mother's milk.
Thus, the importance of breastfeeding is well recognized; however, information about oxytocin, which is necessary for development of the social brain for communication with others, has been fragmentary. Oxytocin in the mother's blood is transferred to the milk. The underlying mechanisms of oxytocin uptake through the digestive tract remained unknown.
The international research team led by researchers of Kanazawa University, Japan, together with researchers of Hokkaido University, Japan, Krasnoyarusk State Medical University, Russia, and the University of California San Francisco, USA, investigated oxytocin uptake from the gut of neonatal mice and obtained the following results.
- Postnatal day 1 mice that stayed with their mother for 20 minutes were found to have oxytocin concentrations in the blood higher than those fasted.
- Postnatal day 1-5 mice that were orally fed with oxytocin showed an increase of oxytocin concentration in the blood up to the fifth day after birth, but it decreased afterwards. Mice administered with oxytocin solution directly into the digestive tract showed an increase of oxytocin concentration in the blood. Accounting for the quantity of blood associated with body weight increase, the increment of oxytocin concentration in the blood is considered to attenuate from postnatal days 5-7.
- Oral administration of oxytocin solution to mice whose receptors for advanced glycation end-products (RAGE) gene (Ager) was knocked out brought about an oxytocin concentration increase in the blood on postnatal days 1-3. However, it sharply decreased on postnatal day 4.
- A clear difference between the wild type mice and the RAGE knockout mice was observed on postnatal days 4-6. This suggests that on postnatal days 1-3, gut closure is not completed and that oxytocin should be freely permeable from the gut in both the wild type and RAGE knockout mice. After the completion of gut closure, the wild type mice expressing RAGE could ingest oxytocin. It was interpreted that on postnatal days 7-8 and after, oxytocin was enzymatically cleaved but could not be absorbed in its intact form.
- In addition, adult mice were examined with a 10-fold quantity of oxytocin administered orally or directly into the digestive tract. It was found that the blood oxytocin level was significantly increased in the wild type mice in a RAGE-dependent manner.
- Mass spectrometry analysis confirmed that oxytocin was transported into the blood in its intact form.
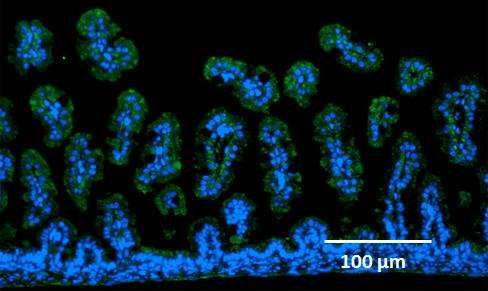
- Expression of RAGE molecules on the surface of intestinal epithelial cells was confirmed by an immunohistochemical study.
The present study concludes that intestinal villiated epithelial cells express RAGE, which is responsible for absorption of oxytocin from the gut into the blood. The present findings indicate that oxytocin is ingested by a specific molecular mechanism and that oxytocin could be orally administered as a medication and/or nutrient (supplement in milk).
More information: Haruhiro Higashida et al, Intestinal transepithelial permeability of oxytocin into the blood is dependent on the receptor for advanced glycation end products in mice, Scientific Reports (2017). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-07949-4