Aggressive breast cancer already has resistant tumour cells prior to chemotherapy
Difficult to treat and aggressive "triple-negative" breast cancer is chemoresistant even before chemotherapy begins, a new study by researchers from Karolinska Institutet and the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center reports. The findings, which are published in the journal Cell, may lead to better and more personalised treatments for breast cancer.
Breast cancer is the most common form of cancer in women and the most common cause of death in middle-aged women in Sweden. Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is an aggressive and difficult to treat form of the disease that makes up about 15 per cent of all breast cancer cases. Chemotherapy is the cornerstone of treatment for TNBC, used either prior to surgery or prophylactically after surgery, as well as for treatment of metastatic disease.
Even though several chemotherapy drugs are effective against TNBC, resistance to treatment is a common problem since it can ultimately lead to relapse and tumour growth. For many years researchers have been trying to understand why such resistance develops and to prevent or reverse it.
Key question
"A key question is whether the resistance develops because of the existence of resistant groups of cells, called clones, in the tumour from the start, or whether tumour cells develop new genetic changes (mutations) during the treatment that cause resistance," says Theodoros Foukakis, Associate Professor at the Department of Oncology-Pathology, Karolinska Institutet, who co-led the study with Associate Professor Nicholas Navin at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, USA.
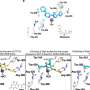
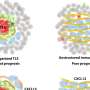
The researchers analysed tumour tissue from 20 patients with TNBC who received preoperative chemotherapy. The tissue was collected before the onset of therapy, after two courses of therapy and on surgery. The researchers used a technique called single-cell sequencing to examine the DNA and gene expression (RNA) of all genes in the individual tumour cells and thus ascertain the cells' properties and kinship.
"The DNA analyses revealed tumour clones remaining after treatment in half of the cases," says Dr. Foukakis. "When we studied them in detail at a single-cell level, we found that these same clones were present in the tumour before chemotherapy, often as a small minority of the tumour cell population."
Single-cell RNA sequencing of thousands of cell nuclei showed that the remaining tumour clones had also adapted their gene expression during treatment to become even more chemoresistant.
"All in all, the study shows that chemoresistance in TNBC is a complex process involving both a selection of resistant clones that existed in the tumour from the start as well as a reprogramming of their gene expression to ensure survival during therapy," concludes Dr. Foukakis.
The results may provide a basis for future studies to identify therapy-resistant tumour clones and thus personalise treatment for breast cancer patients who respond poorly to chemotherapy and have a worse prognosis.
More information: Charissa Kim et al. Chemoresistance Evolution in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Delineated by Single-Cell Sequencing, Cell (2018). DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.03.041