How nature, nurture shape the sleeping brain
Some patterns of electrical activity generated by the brain during sleep are inherited, according to a study of teenage twins published in JNeurosci. Pinpointing the relative contributions of biology and experience to sleep neurophysiology could inform therapies for numerous psychiatric disorders in which alterations in brain activity during sleep can be detected.
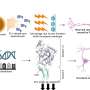
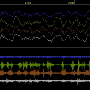
Leila Tarokh and colleagues used electroencephalography to measure the brain activity of 11- to 14-year-old pairs of identical and fraternal twins during two consecutive nights of sleep at home.
This study design allowed the researchers to tease apart the influence of genetic and environmental factors on brain activity during sleep.
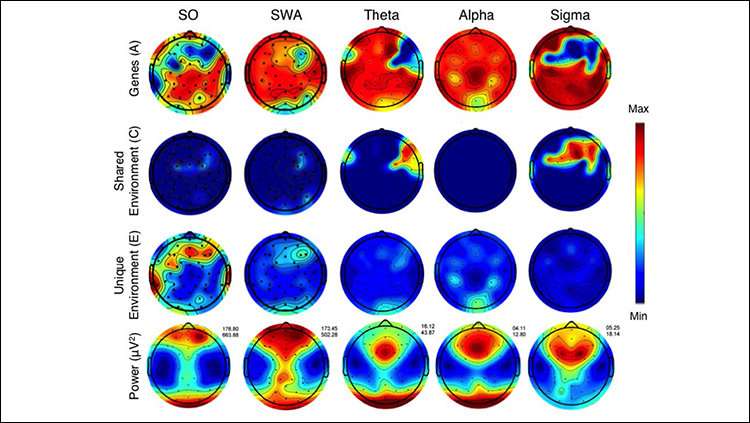
They found both types of factors shape two patterns of activity—slow waves and spindles—that are crucial for core functions of sleep, including memory consolidation.
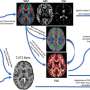
The influence of genes and environment on this activity depended on the brain region in question, with frontal regions being under strong environmental control and regions toward the back of the brain under stronger genetic control.
More information: Nature and Nurture: Brain region specific inheritance of sleep neurophysiology in adolescence, JNeurosci (2018). DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0945-18.2018