New study reveals potential therapeutic approach to enhance keratinocyte migration in cutaneous wound healing

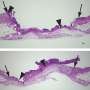
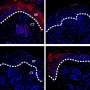
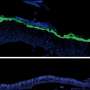
Researchers have identified a new mechanism involving ginsenoside Rb1, which has the ability to stimulate keratinocyte migration and promote cutaneous wound healing. They report the results of a study showing that Rb1 enhances keratinocyte migration in an article published in Journal of Medicinal Food, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The researchers demonstrated that Rb1 significantly increases the production of sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), which is a signaling factor in keratinocytes known to stimulate wound repair through greater keratinocyte migration.
More information: Kyong-Oh Shin et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 Enhances Keratinocyte Migration by a Sphingosine-1-Phosphate-Dependent Mechanism, Journal of Medicinal Food (2018). DOI: 10.1089/jmf.2018.4246