Researchers report vision-based neurotransmitter events for the first time
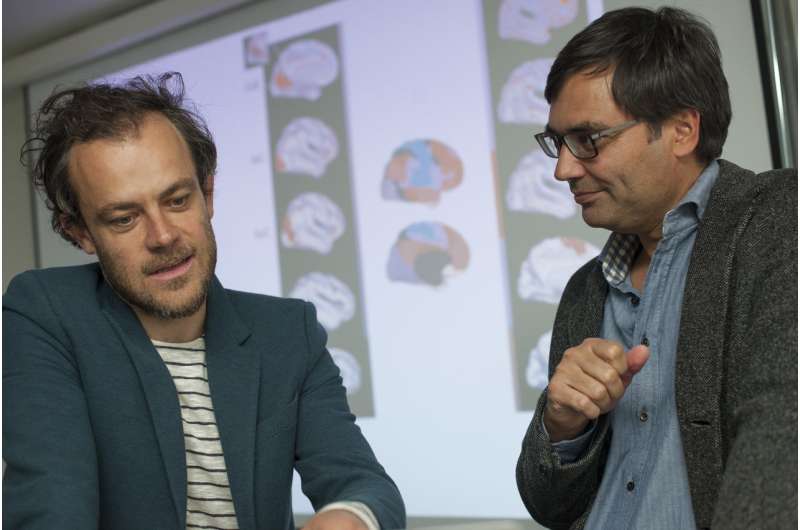

How does vision work, and what happens in the brain during the process? As simple as this question may sound, it has yet to be scientifically clarified. Dr. Valentin Riedl of the Technical University of Munich (TUM) and his team have now been able to show that the distribution of the two most important neurotransmitters in the brain changes as soon as we open our eyes, regardless of whether we actually see anything.
To communicate with each other, neurons use chemical messengers known as neurotransmitters. The two most important neurotransmitters in the human brain, glutamate and GABA, have opposing effects: glutamate activates neurons, while GABA suppresses them. By altering the concentrations of the two neurotransmitters, the brain is able to process visual stimuli from the eyes.
Privatdozent Dr. Valentin Riedl, research group leader in the Neuroradiology Department of University Hospital rechts der Isar of the TUM, and his team have studied how the concentrations of the two neurotransmitters change in the visual cortex, the region in the brain responsible for vision. The team used magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) to measure the concentrations of the neurotransmitters in detail.
Visual process triggered by opening the eyes
The experiment consisted of three phases. The subjects first lay in the dark for five minutes with their eyes closed. They then opened their eyes and stared into the darkness. Finally, they were shown a checkerboard pattern that blinked on and off rapidly. Throughout the experiment, the concentrations of both neurotransmitters in the visual cortex were measured simultaneously.
In the resting state with the eyes closed, GABA levels were high. Surprisingly, however, concentrations of this inhibitory neurotransmitter decreased as soon as the subjects opened their eyes, despite the fact that there was still nothing to see. "The brain prepares for forthcoming stimuli as soon as the eyes are opened. This phenomenon had never previously been observed, because other studies had not measured this state," Riedl says. Only when an actual visual stimulus was perceived, i.e. the blinking checkerboard pattern, did the concentration of glutamate, the activating neurotransmitter, increase.
Data consistent with fMRT measurements
For the first time, the researchers also compared their MRS data with data obtained by functional MRI (fMRI), a common method for visualizing human brain activity. In this technique, the consumption of oxygen is measured in specific brain regions. A high consumption is an indirect indicator of neuronal activity in a given area.
They found that changes in neurotransmitter levels in the visual cortex coincided with evidence of brain activity in the fMRI scans. "The results of the two methods agreed perfectly. By combining the two techniques, we're not only able to say that there is increased activity in a region; for the first time, we're also able to specifically attribute that activity to the two neurotransmitters," Riedl explains.
The findings by Riedl and his team also have clinical relevance. For example, it is suspected that the distribution of the two neurotransmitters is permanently disturbed in psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia. "To date, however, there is no proof of this. An examination using both spectroscopy and fMRT would provide much more precise and far-reaching information on the concentrations of the neurotransmitters in patients," Riedl says.
More information: Katarzyna Kurcyus et al, Opposite Dynamics of GABA and Glutamate Levels in the Occipital Cortex during Visual Processing, The Journal of Neuroscience (2018). DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1214-18.2018