Parasites from patients with cerebral malaria stick preferentially in their brains
A team at LSTM with their collaborators in Malawi and Denmark have provided, for the first time, evidence which links the ability of red blood cells infected with the malaria parasite to bind to the cells lining the blood vessels of the brain, with the clinical syndrome cerebral malaria.
Cerebral malaria is a life-threatening complication of infection with the parasite Plasmodium falciparum. This complication is characterised by the parasite infected red blood cells accumulating in the brain and occurs in 1 to 2 percent of the over 200 million reported cases of malaria.
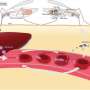
First author on the paper, published recently in the journal EMBO Molecular Medicine, Dr. Janet Storm, explained: "Very little is known about why this serious complication occurs in some children but not others. However, it is understood that infected red blood cells, presenting with a protein called P. falciparum erythrocyte membrane protein 1 (PfEMP1) on its surface bind to host cells lining the blood vessels in many organs, including the brain."
A property of the PfEMP1protein is its variability, which results in changes in the ability of infected red blood cells to bind to host cells in the brain. This has been suggested as the reason we only see cerebral malaria in some infected individuals, and if the infected red blood cells do not bind in the brain cerebral malaria cannot occur.
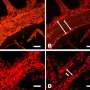
In their lab in at MLW in Malawi, the team utilised a flow-based adhesion assays to study the binding of infected red blood cells from children with cerebral or uncomplicated malaria to cells derived from human brain blood vessels. The team also used molecular techniques to study the PfEMP1 expressed by the infected red blood cells.
Results showed that binding of infected red blood cells from patients with cerebral malaria to the brain-derived cells was higher than that seen from patients with uncomplicated malaria. This suggests that in most cases P. falciparum avoids targeting the brain and that cerebral malaria only occurs when red blood cells express a subset of PfEMP1 proteins with particular adhesion phenotypes which allow for efficient binding to the cerebral blood vessels. Knowing that binding in the brain is a key feature of cerebral malaria allows researchers to focus their attention on developing new interventions for severe disease based on the interaction between infected red blood cells and the host cells lining the blood vessels in the brain.
More information: Janet Storm et al. Cerebral malaria is associated with differential cytoadherence to brain endothelial cells, EMBO Molecular Medicine (2019). DOI: 10.15252/emmm.201809164