Oxytocin could help treat alcohol use disorder
The neuropeptide oxytocin blocks enhanced drinking in alcohol-dependent rats, according to a study published April 16 in the open-access journal PLOS Biology led by Drs. Tunstall, Koob and Vendruscolo of the National Institutes of Health, and Drs. Kirson and Roberto of The Scripps Research Institute. Targeting the oxytocin system, the authors note, may provide novel pharmaceutical interventions for the treatment of alcohol-use disorder.
Administering oxytocin can decrease consumption, withdrawal symptoms, and drug-seeking behavior associated with several drugs of abuse, and shows promise as a pharmacological approach to treat drug addiction. But first, researchers need to understand how oxytocin mediates these effects in animal models.
To address this question, Tunstall and colleagues tested the hypothesis that oxytocin administration could normalize the maladaptive brain changes that occur in alcohol dependence and thereby reduce alcohol drinking in an established rat model of alcohol dependence.
The authors investigated oxytocin's effects on dependence-induced alcohol consumption and altered signaling of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA in the central nucleus of the amygdala (CeA)—a key brain region in the network affected by alcohol dependence.
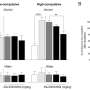
The experiments demonstrated that oxytocin administered systemically, intranasally or into the brain blocked excess drinking in alcohol-dependent but not in normal rats. Moreover, oxytocin blocked GABA signaling in the CeA. Taken together, these results provide evidence that oxytocin likely blocks enhanced drinking by altering CeA GABA transmission.
These results provide evidence that aberrations in the oxytocin system may underlie alcohol use disorder and that targeting this system, possibly by intranasal administration, could prove a promising therapy in people who misuse alcohol.
More information: Tunstall BJ, Kirson D, Zallar LJ, McConnell SA, Vendruscolo JCM, Ho CP, et al. (2019) Oxytocin blocks enhanced motivation for alcohol in alcohol dependence and blocks alcohol effects on GABAergic transmission in the central amygdala. PLoS Biol 17(4): e2006421. doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.2006421