First-in-human trial for new lung cancer immunotherapy
Cancer Research UK and Vaccitech Oncology Limited (VOLT), today (Wednesday) announce a new partnership to bring a novel immunotherapeutic vaccine strategy to patients with lung cancer.
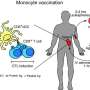
The vaccine treatment developed by VOLT, a strategic collaboration between Vaccitech Ltd and the Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research, is designed to stimulate the body's immune system to attack cancer cells. It will deliver cancer-associated antigens (MAGE A3 and NY-ESO-1) to antigen presenting cells called dendritic cells, causing the immune system to produce cytotoxic T cells, which target and kill cancerous cells expressing the antigens.
This is the first time a viral vaccine program using this platform will be tested in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), the most common type of lung cancer. And separate clinical trials are also ongoing to test similar recombinant virus vaccines to treat people with late-stage prostate cancer.
Cancer Research UK's Centre for Drug Development (CDD) will sponsor and manage the first clinical trial of the therapeutic vaccine strategy, in combination with current standard of care and first line treatment for NSCLC. The Phase I/IIa trial will investigate whether receiving the immunotherapeutic improves the efficacy of chemotherapy and anti-PD-1 treatment. It will also assess the ability of the therapeutic to provoke a safe and effective anti-cancer immune response in people with NSCLC.
Dr. Nigel Blackburn, Cancer Research UK's director of drug development, said: "This partnership with VOLT is an important step to help accelerate this promising immunotherapy and could help more people survive lung cancer, which remains very hard to treat. This novel approach using a modified adenovirus to prime the immune system and alert it to the presence of cancer cells could offer a completely new way to treat the disease."
Vaccitech CEO, Bill Enright, said: "We are delighted to enter into a clinical development partnership with two of the world's most prestigious cancer research institutions. We believe that this partnership is an important validation of our prime boost platform's utility in oncology as well as infectious disease."
Jonathan Skipper, executive vice president for technology development, Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research, said: "Previous clinical trials of experimental cancer vaccines targeting MAGE and NY-ESO antigens have demonstrated that these antigens are highly specific to cancer and capable of eliciting strong immune responses. We believe that Vaccitech's highly effective T cell induction platform should provide a potent immunotherapeutic that, in combination with checkpoint blockade, is capable of inducing sustained levels of cancer antigen-specific CD8+ T cells and the desired therapeutic effect in patients."
Upon trial completion, VOLT retains the option to undertake further clinical development and commercialization of the immunotherapeutic. If VOLT elects not to exercise its option, Cancer Research UK will have the rights to take the program forward in all cancer indications.
The trial will enroll approximately 80 people who have been diagnosed with NSCLC and is due to start at the end of 2020. It will be conducted across multiple sites in the UK, through the Experimental Cancer Medicine Centre (ECMC) network.
Every year around 41,700 people are diagnosed with NSCLC in the UK, which accounts for around 88% of all lung cancer cases. New treatments are urgently needed, as only around 5% of people survive lung cancer for 10 years or more in the UK.
More information: Vaccination in Prostate Cancer (VANCE) clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02390063
Vaccination in Early and Advanced Prostate Cancer (ADVANCE) clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NC … ADVANCE+trial&rank=1