West African HIV-2 prevalence associated with lower historical male circumcision rates
In West African cities, male circumcision rates in 1950 were negatively correlated with HIV-2 prevalence from 1985, according to a study published December 7, 2016 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by João Sousa from the University of Leuven, Belgium, and colleagues.
The HIV-2 virus likely emerged in humans around 1930-40 and is less widespread than the predominant HIV-1, remaining mostly within West Africa. Whilst male circumcision is known to be associated with reduced HIV-1 prevalence, because the foreskin is highly vulnerable to infection, the association between male circumcision and HIV-2 prevalence had not previously been examined.
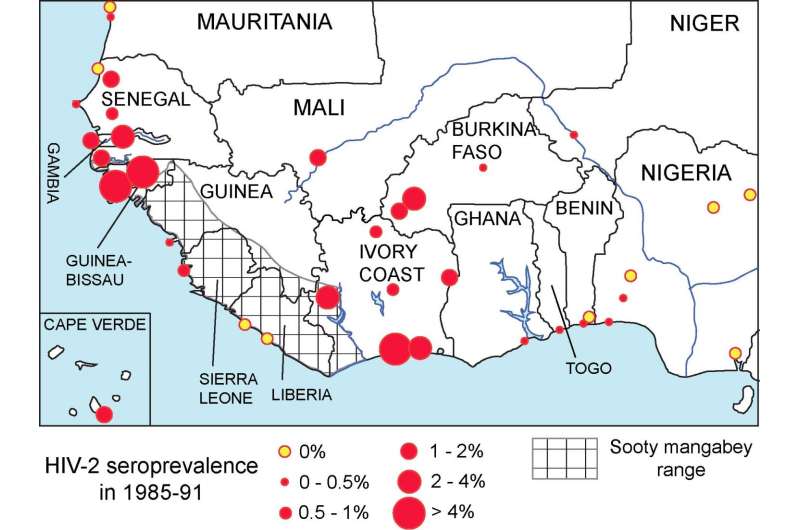
The authors of the present study gathered the published results of large scale HIV-2 serosurveys, conducted from 1985 onwards, of the populations of 30 West African cities. They combined estimates of historical male circumcision frequency in 218 West African ethnic groups with demographic data to estimate male circumcision frequency for each West African city at various time points. The researchers then matched HIV-2 prevalence with the estimated male circumcision frequency in each city to identify any correlation.
The authors found that cities with higher male circumcision rates in 1950 generally tended to have lower HIV-2 prevalence at the time of the first serosurveys in 1985-91. Generally, male circumcision was far less common than it is today, and varied more by country. Cities in two countries, Guinea-Bissau and Côte d'Ivoire, which are thought to have acted as epicenters during the emergence of HIV-2, had particularly low male circumcision rates, reinforcing the negative correlation.
Whilst the data on male circumcision and HIV-2 prevalence were obtained in different years, making it difficult to link the two directly, the authors state that HIV-2 may only have been able to achieve high prevalence in West African cities where a substantial proportion of the population was uncircumcised.
"Lack of circumcision may have been a driving factor in initial HIV-2 emergence," says Sousa.
More information: Sousa JD, Temudo MP, Hewlett BS, Camacho RJ, Müller V, Vandamme A-M (2016) Male Circumcision and the Epidemic Emergence of HIV-2 in West Africa. PLoS ONE 11(12): e0166805. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166805